2.Defend your answer by delineating the difference between substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation with suitable examples.
Substrate-level phosphorylation:
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a metabolic process that produces ATP or GTP by directly transferring a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP or GDP.
Examples of common substrate level phosphorylation reactions:
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + ADP → 3-phosphoglycerate + ATP
Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP → pyruvate + ATP
Acetyl phosphate + ADP → acetate + ATP (same mechanism for other alkanoic acids)
Succinyl CoA + NDP → succinate + NTP + CoASH (N = G or A)
Oxidative phosphorylation:
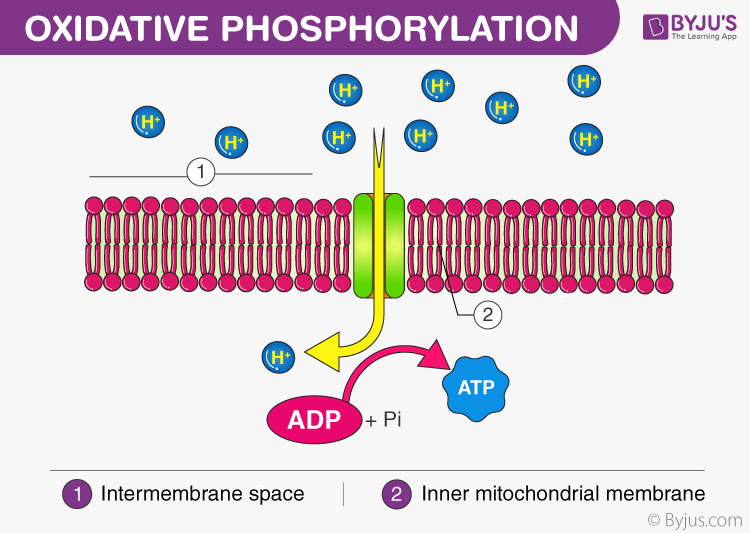
The mechanism through which ATP generation is linked to the flow of electrons along the mitochondrial electron transport chain and the accompanying consumption of oxygen is known as oxidative phosphorylation.
Oxidative Phosphorylation Definition
“Oxidative phosphorylation is the process of ATP formation, when electrons are transferred by electron carriers from NADH or FADH2 to oxygen”
What is Oxidative Phosphorylation?
Oxidative phosphorylation is the final step in cellular respiration. It occurs in the mitochondria. It is linked to a process known as electron transport chain. The electron transport system is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The electrons are transferred from one member of the transport chain to another through a series of redox reactions.

Comments
Post a Comment